Case #3 Answers & Discussion
Contributed by Dr. Duy
Your Score and Answers
| Question | Correct Answer | Your Answer | Your Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| What other finding is likely to be present? | Peripheral eosinophilia | 1/1 | |
| This patient most likely has which of the following? | Gastroesophageal reflux | 1/1 | |
| This patient most likely has which of the following? | Leiomyoma | 1/1 | |
| What is the difference between fluoroscopic images and diagnostic radiographs? | Fluoroscopy uses lower mA | 1/1 |
Findings
You can view the full interactive case here.
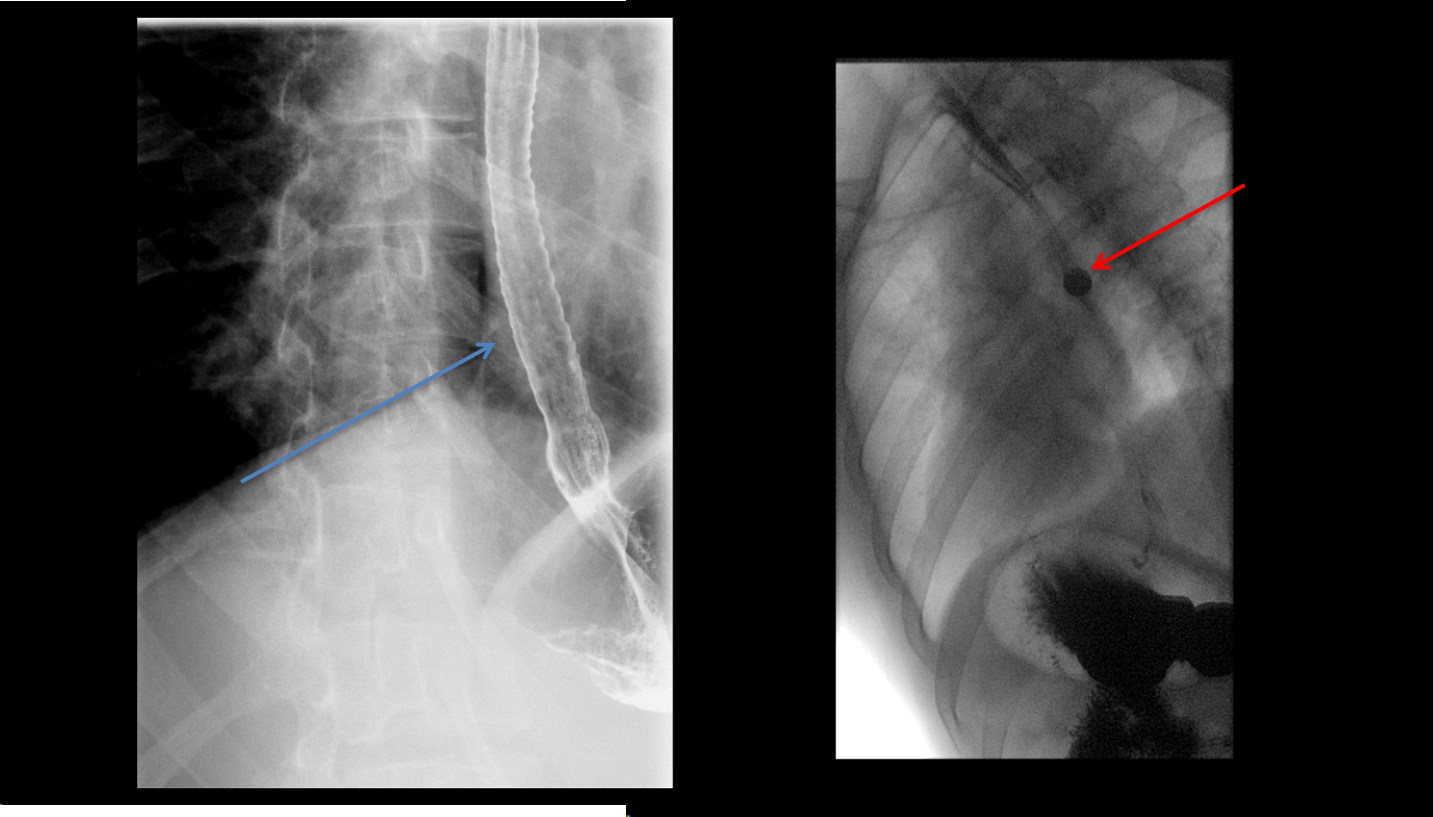
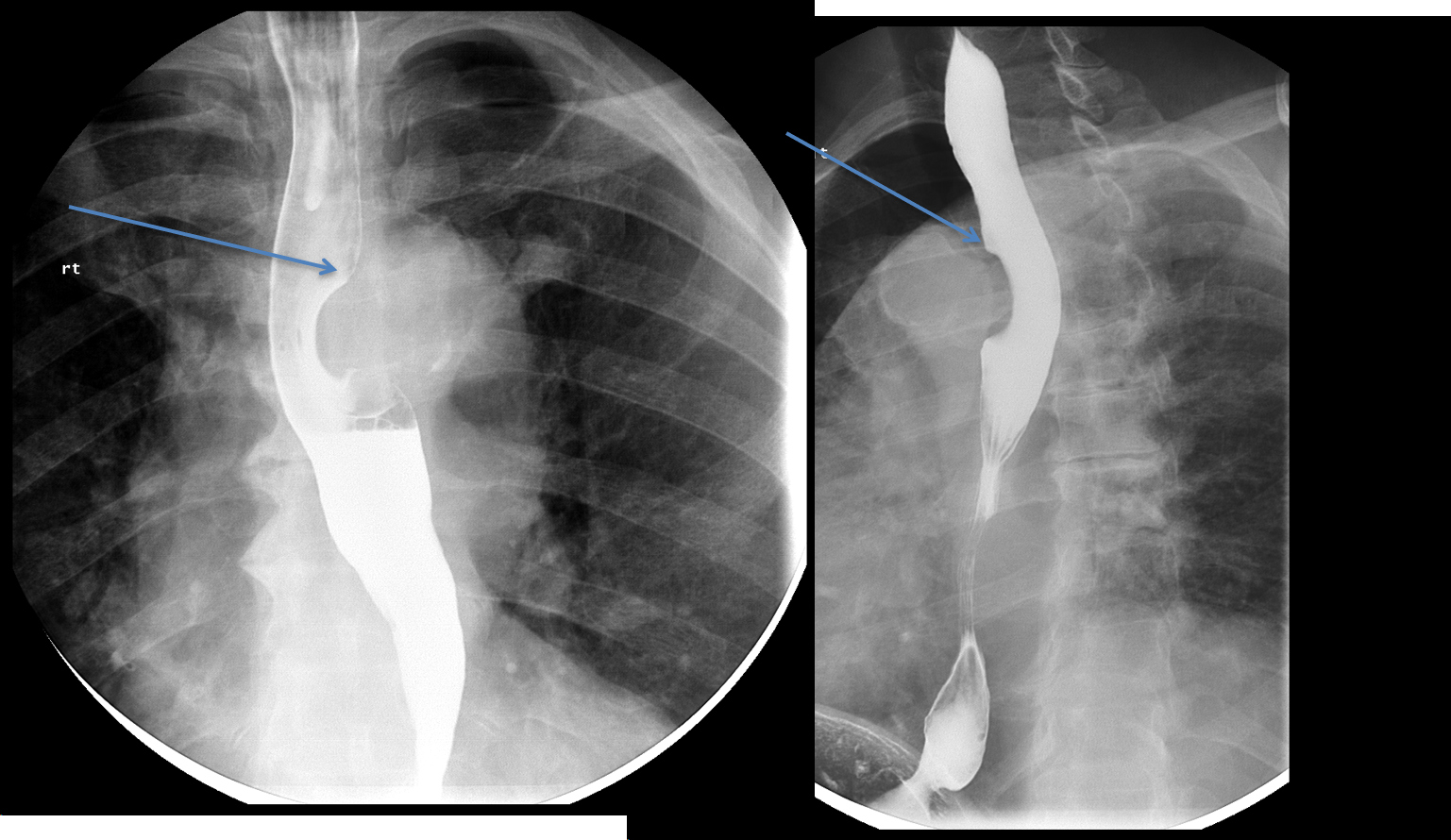
Esophagus with long segment narrowing, with corrugated appearance (blue arrow). 13 mm barium pill is unable to traverse the stricture (red arrow).
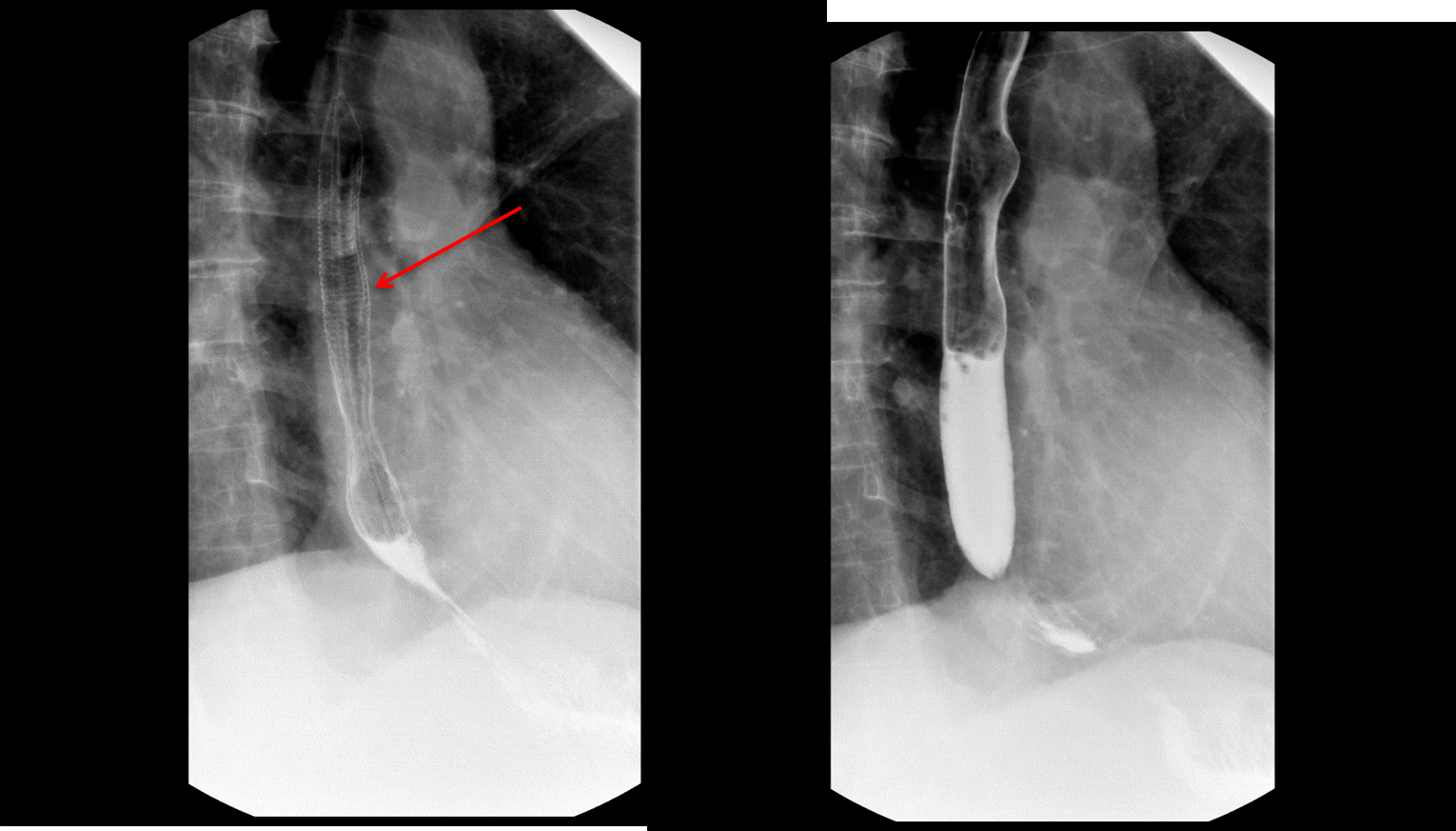
Esophagram shows fine circumferential folds (arrow) which do not persist and are not seen on the subsequent image.
Eosinophilic esophagitis
- Most commonly seen in males age 20-40
- Presents with dysphagia
- Etiology is unknown, but possibly a type of allergic reaction
- Findings on barium swallow include strictures, webs, and spasms.
- Ringed esophagus is classic, however long strictures can also be seen.
- Rings are fixed, not transient
- Peripheral eosinophilia can be seen on CBC.
Feline esophagus
- Transient, fine transverse folds in the esophagus
- Due to muscular contractions
- Does not persist
- Almost always seen in the setting of gastroesophageal reflux
Submucosal esophageal masses
- The differential of esophageal masses is different depending on appearance
-
Submucosal lesions usually have smooth, obtuse margins with the esophagus, like this case.
-
- Differential is broad, and includes leiomyoma, duplication cyst, GIST, as well as hematoma.
Physics Discussion
- Radiographs use higher mAs for short durations. Fluoroscopy uses lower mAs for long durations, which prevents the tube from overheating.
- Radiographs provide higher spatial resolution and higher signal to noise ratio.
- A fluoroscopic frame has a lower dose than a radiograph.
- Note that spot images acquired during a fluoroscopic study are the same as radiographs.
References
- Dysphagia Revisited: Common and Unusual Causes Laura R. Carucciand Mary Ann Turner RadioGraphics2015 35:1, 105-122
- Huda W. Review of Radiologic Physics. 4 ed: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; (2016).