Case #8 Answers & Discussion
Contributed by Dr. Duy
Your Score and Answers
| Question | Correct Answer | Your Answer | Your Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is the most likely diagnosis? | Tubal ectopic | 0/1 | |
| What is the most likely diagnosis | Spontaneous abortion in progress |
0/1 | |
| Which of the following is true regarding the viability of this pregnancy? | The viability of this pregnancy is uncertain |
0/1 | |
| Which of the following is true regarding the viability of this pregnancy? | The pregnancy is nonviable | 0/1 | |
| What mode is indicated by the arrow? | M-mode | 0/1 |
Findings
- Case #1
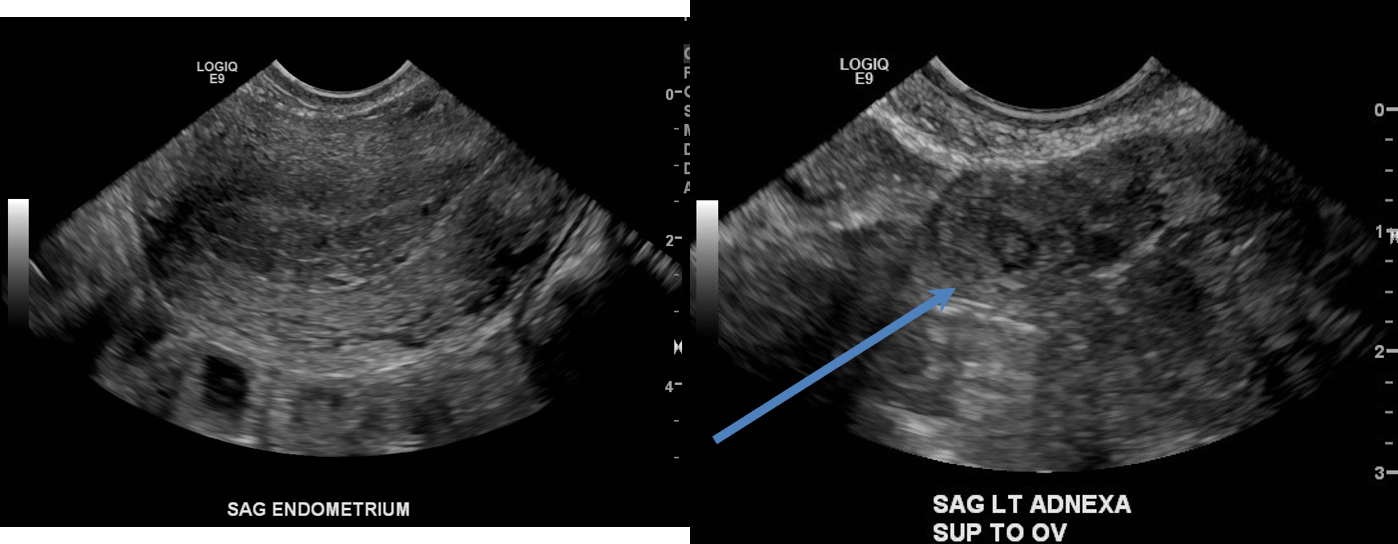
- No intrauterine pregnancy is identified. There is a mass with an echogenic rim in the left adnexa separate from the ovary (blue arrow). Cine images showed cardiac motion.
- Case #2
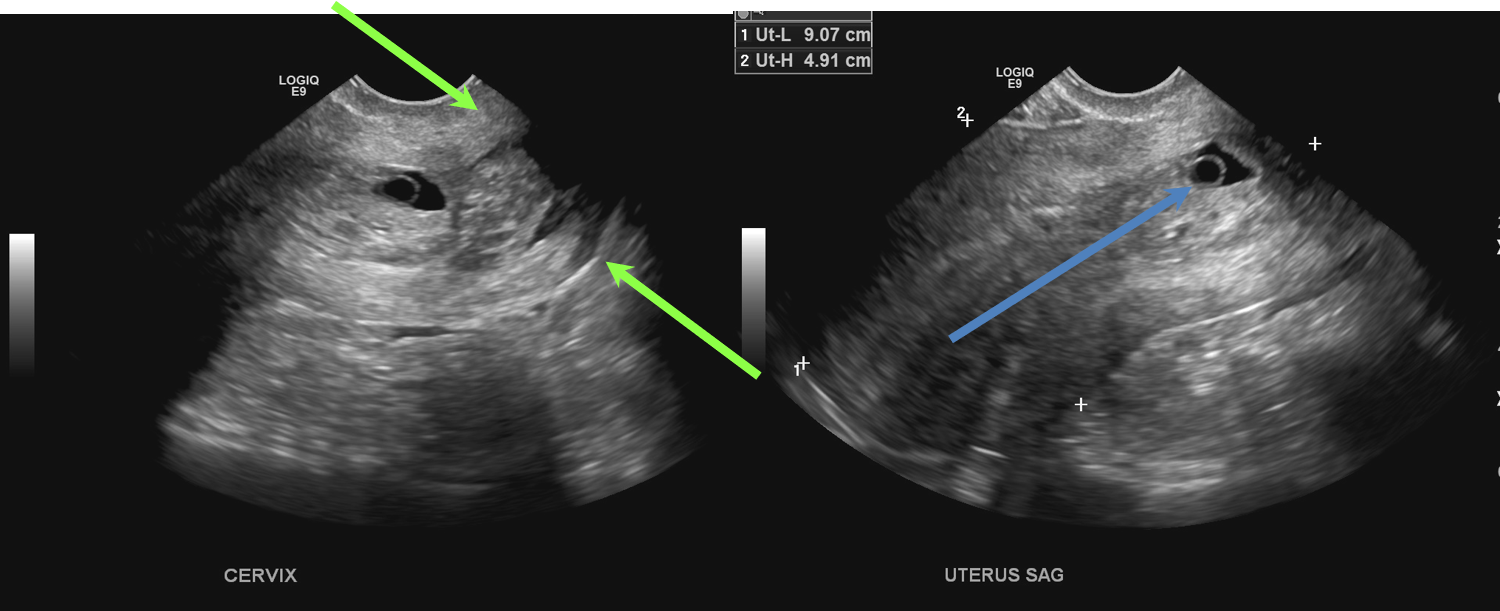
- A gestational sac and a yolk sac (blue arrow) are seen in the endocervical canal. There are blood products in the canal. The cervix is open (green arrows).
- Case #3
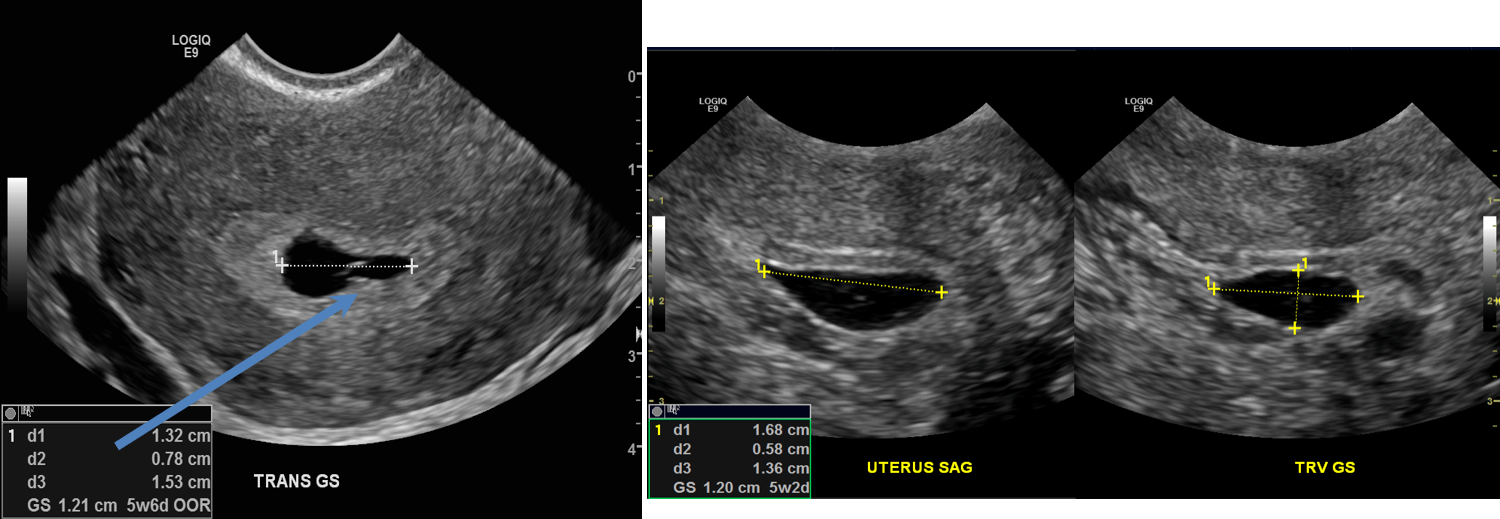
- Initial images show a gestational sac and a yolk sac (blue arrow). Follow-up ultrasound (image on the right) showed a gestational sac that was similar in size. No heartbeat was identified.
Ectopic Pregnancy
- 95% occur in the fallopian tube. Other locations are interstitial, cornual, ovarian, and cervical.
- Findings of a tubal pregnancy include an adnexal mass outside the ovary.
- A yolk sac or embryo may or may not be seen
- The mass should move separately from the ovary.
- Tubal ring sign has also been described as a an echogenic ring of soft tissue with “ring of fire” flow pattern on color Doppler
- A normal corpus luteum can also have this appearance within the ovary.
- Cervical ectopic can sometimes be difficult to differentiate from a spontaneous abortion in progress
- An open cervix can sometimes be seen with an abortion in progress
- If in doubt, recommend close follow-up and repeat HCGs.
What to do if no pregnancy is seen
Ultrasound modes
- A-mode is amplitude mode.
- This mode is most commonly used for ophthalmologic applications
- B-mode is brightness mode.
- This mode displays a 2d image of echo intensity.
- This is the mode used for grayscale images.
- M-mode is motion mode.
- A single scan line is used.
- This shows the distance from the transducer of an object over time.
- This is used primarily in echocardiography
References
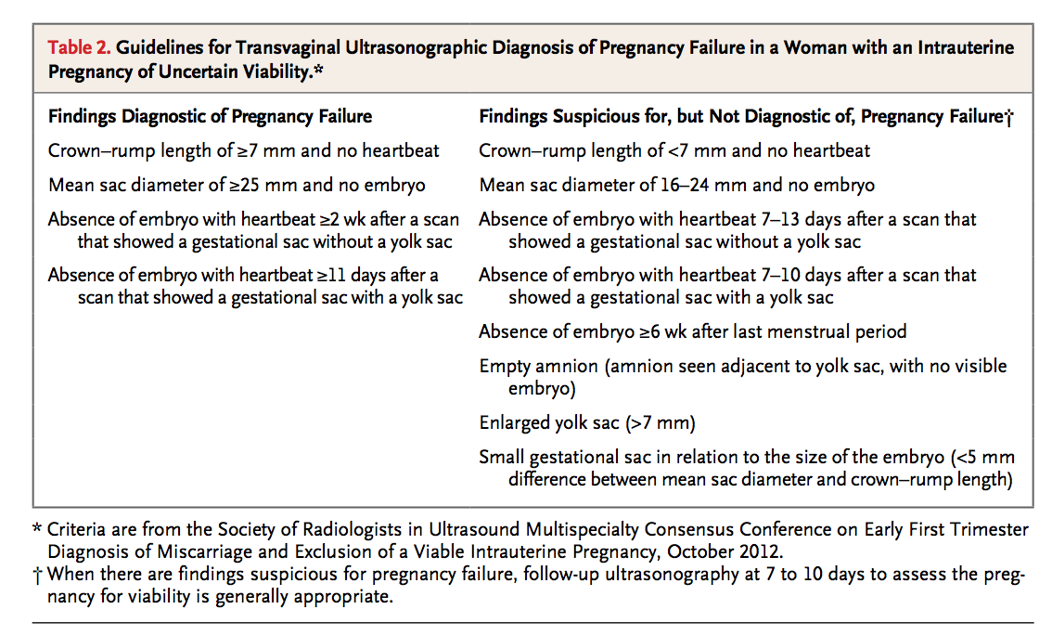
- Doubilet PM, Benson CB, Bourne T, Blaivas M. Diagnostic Criteria for Nonviable Pregnancy Early in the First Trimester. NEJM 2013; 369(15): 1443-1451.
- Lin EP, Bhatt S, Dogra VS. Diagnostic clues to ectopic pregnancy. Radiographics 2008; 28(6): 1661-1671.
- Hangiandreou NJ. AAPM/RSNA physics tutorial for residents: topics in US. Radiographics 2003; 23(4): 1019-1033.