Age: 8 months
Sex: Female
Indication: Evaluate for tethered cord
Save ("V")
Lipomyelocele
Findings
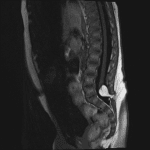
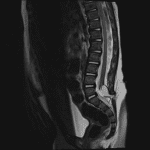
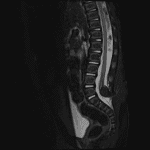
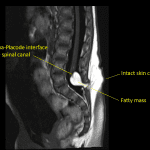
- Low-lying spinal cord terminating at the level of L5
- Associated T1/T2 hyperintense mass measuring 14 x 12 x 12 mm with signal suppression on STIR. This mass extends from the neural placode posteriorly through a spinal canal defect into the posterior paraspinal soft tissues
- Sacral spinal dysraphism
Diagnosis
- Lipomyelocele
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Low-lying spinal cord terminating at the level of L5. Associated T1/T2 hyperintense mass measuring 14 x 12 x 12 mm with signal suppression on STIR, suggesting fatty composition. This mass extends from the neural placode posteriorly through a spinal canal defect into the posterior paraspinal soft tissues. These findings are consistent with a lipomyelocele.
Sacral spinal dysraphism.
Discussion
- Neural tube defects can be complicated to understand and distinguish
- Try thinking about them in groups of conditions resulting from failures of different steps of neurulation (see below diagrams):
- Normal neurulation occurs during the third and fourth weeks of gestation as the neural tube forms within and then separates from the ectoderm
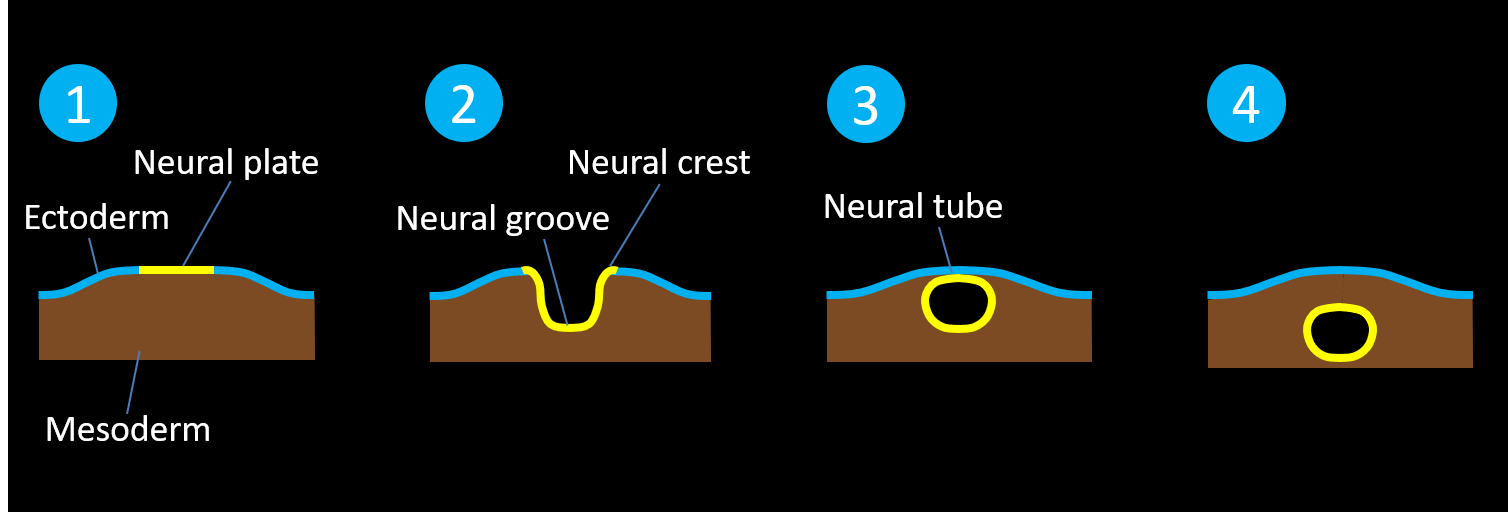
-
-
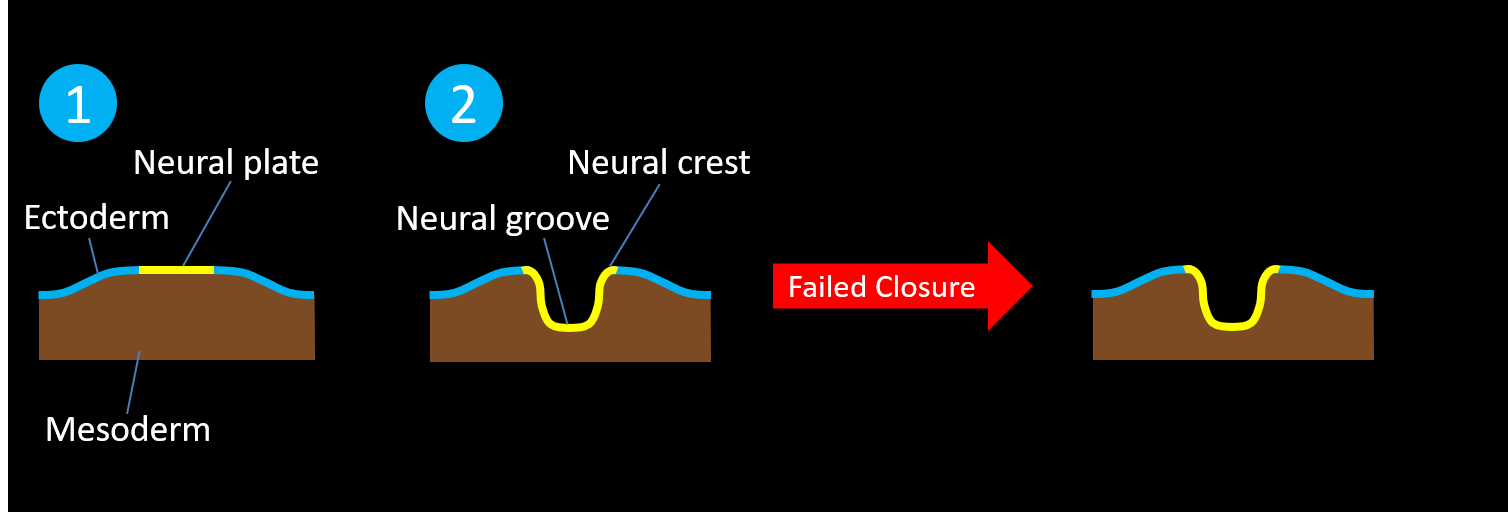
- Failed closure and failed separation of the neural tube from the ectoderm results in open neural tube defects (i.e. defects with no skin covering), including:
- Myelomeningocele – the meningeal lining and the neural placode extend beyond the skin surface
- Myelocele – the neural placode remains flush with skin surface
- Failed closure and failed separation of the neural tube from the ectoderm results in open neural tube defects (i.e. defects with no skin covering), including:
-
-
-
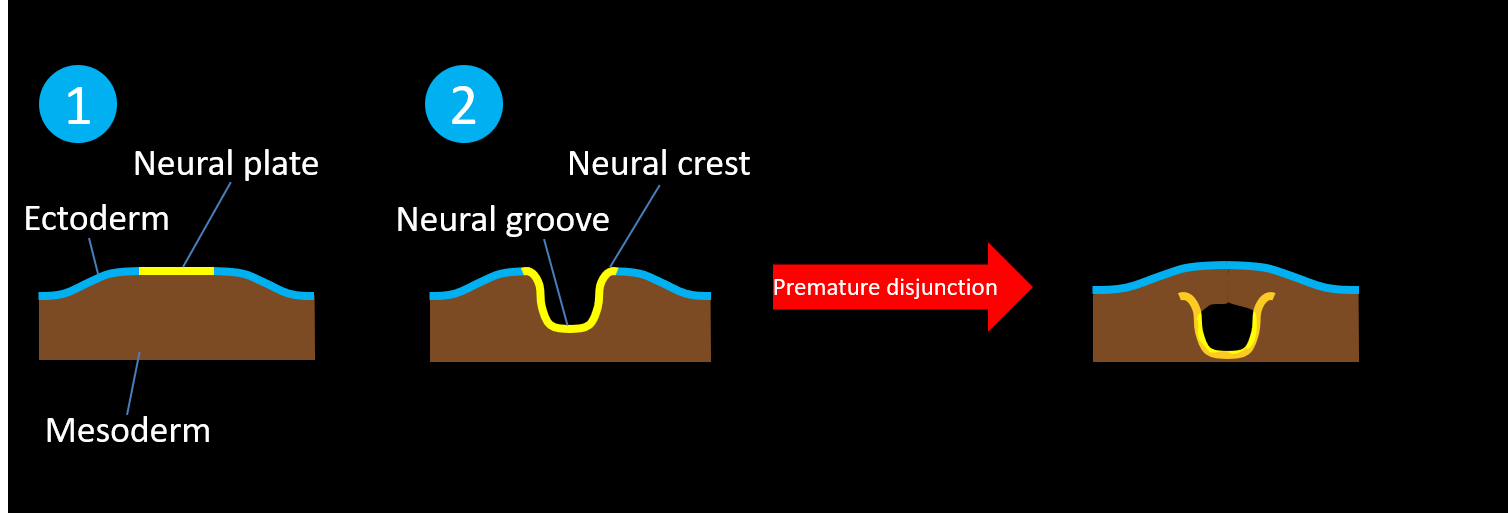
- Premature disjunction results in closed neural tube defects (i.e. defects with skin covering) where mesodermal elements are interposed within an incompletely closed neural tube that separates from the ectoderm, including:
- Lipomyelomeningocele – lipoma-placode interface located outside of the spinal canal
- Lipomyelocele – lipoma-placode interface located inside of the spinal canal
- Meningocele – meningeal lining herniates through a spinal canal defect without herniation of neural elements
- Terminal myelocystocele – syringocele herniates into a meningocele
- Premature disjunction results in closed neural tube defects (i.e. defects with skin covering) where mesodermal elements are interposed within an incompletely closed neural tube that separates from the ectoderm, including:
-
-
-
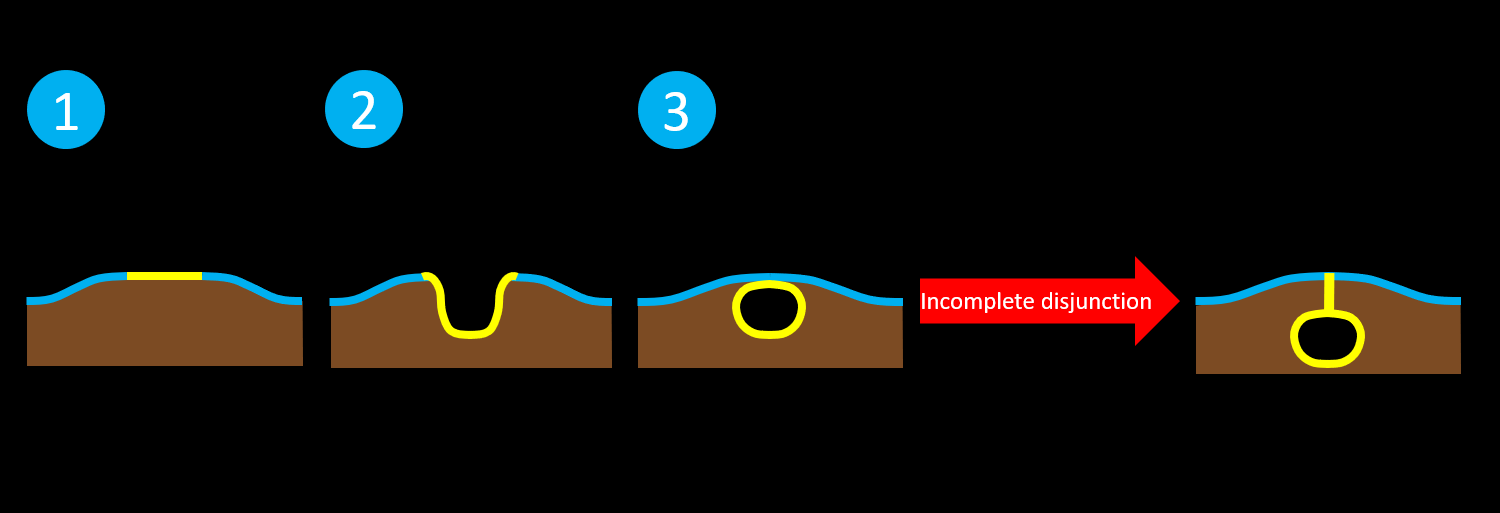
- Incomplete disjunction results in a closed neural tube defect with a persistent dermal sinus attached to the neural tube
- May have associated intradural dermoid or epidermoid lesions
- Incomplete disjunction results in a closed neural tube defect with a persistent dermal sinus attached to the neural tube
-
-
-
- Additional disorders of abnormally located mesodermal elements can result in intradural lipomas without associated dural defects
-
- This case is an example of a lipomyelocele because there is an intact skin covering, a fatty mass extending through a spinal canal defect, and the lipoma-placode interface is located within the spinal canal


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
