Age: 75
Sex: Male
Indication: Fall
Save ("V")
Case #3
You must be logged in to submit this form.
Findings
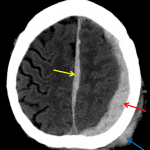
- Acute subdural hematoma layering over the left cerebral convexity with a smaller portion extending over the left tentorium and interhemispheric falx
- Diffuse left cerebral hemispheric sulcal effacement with left to right midline shift
- Left posterior scalp hematoma
- Right medial orbital wall blow-out fracture without hemorrhage in the adjacent ethmoid air cells or extraconal fat. No extraocular muscle herniation
- Incidental note is made of dolichoectasia of the vertebral and basilar arteries
Diagnosis
- Acute subdural hematoma
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Acute subdural hematoma measuring up to 10 mm in thickness layering over the left cerebral convexity with a smaller portion extending over the tentorium and interhemispheric falx. This results in diffuse left cerebral hemispheric sulcal effacement with 6 mm left to right midline shift. Basal cisterns are patent without evidence of uncal or cerebellar tonsillar herniation.
Left posterior scalp hematoma without subjacent calvarial fracture.
Right medial orbital wall blow-out fracture without hemorrhage in the adjacent ethmoid air cells or extraconal fat, favoring a remote fracture. No extraocular muscle herniation.
Discussion
- Subdural hematomas accumulate between the dura and arachnoid mater
- These are seen more commonly than epidural hematomas and often occur in the elderly, though they are also seen with nonaccidental trauma in infants and in trauma across all ages
- Subdural hematomas result from venous bleeding, typically due to rupture of bridging cortical veins which traverse the potential subdural space on their way to the dural venous sinuses
- There is a less common association with skull fractures
- Though not always easy to tell apart from epidural hematomas, favor subdural hematoma if:
- A hematoma crosses suture lines but respects midline (epidural hematomas respect suture lines unless there is a fracture through a suture or sutural diastasis)
- A hematoma is crescent-shaped rather than lens-shaped and layers along the entire cerebral convexity or extends along the falx or tentorium
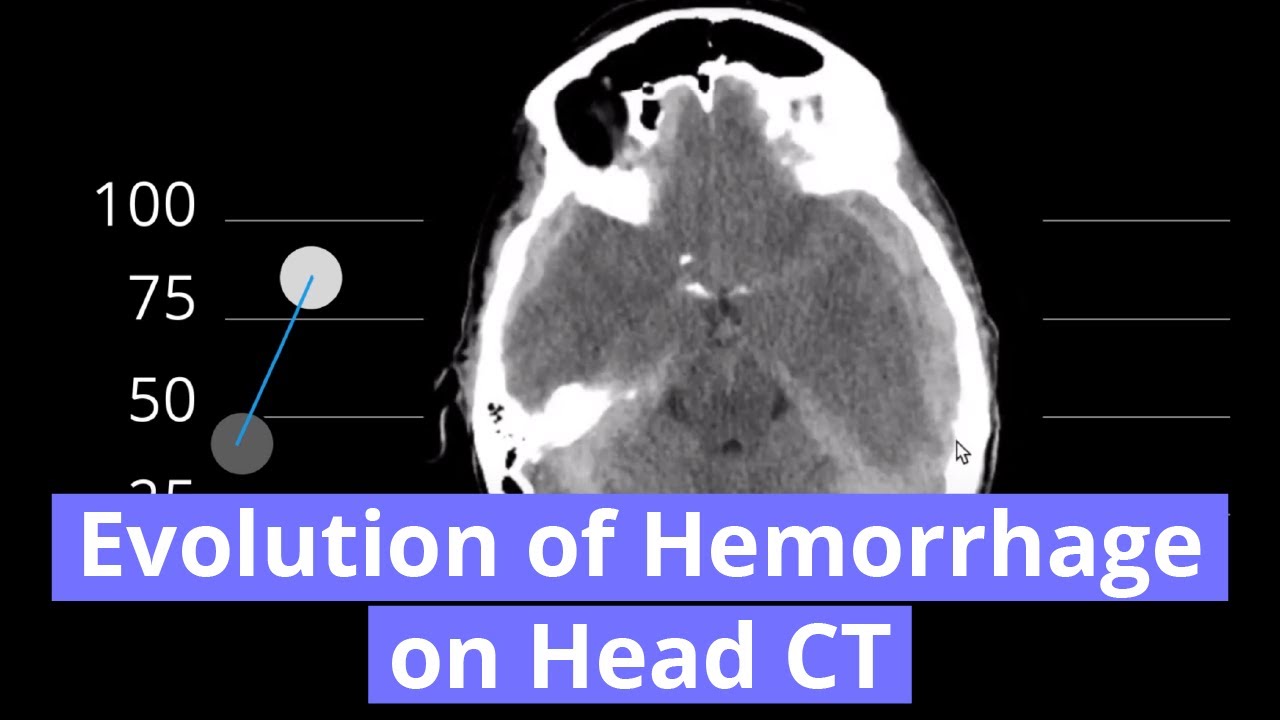
- Here is the typical progression of density of blood products on noncontrast CT (*please note that these are estimates that can vary from case to case and can be substantially altered in the setting of coagulopathy; also if the patient is anemic, even acute blood may not be very dense appearing*)
- Hyperacute (< 1 hr) – hypodense (unclotted blood)
- Acute (hours to weeks) – hyperdense
- Subacute (~2-4 weeks) – isodense to cortex – these are really tough to see
- Chronic (months) – hypodense to cortex and eventually isodense to CSF
- Always mention fractures even if you are pretty sure they are old (like the medial orbital wall fracture in this case). Sometimes acute fractures can fool you by not having much surrounding edema/hemorrhage
- Scalp contusions and hematomas often go together. Although not a strict rule, contusions are typically less well defined (these represent edema secondary to tissue damage and often cause subcutaneous fat stranding) and hematomas are often more hyperattenuating and demarcated



 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
