Age: 9
Sex: Female
Indication: Fall
Save ("V")
Case #2
You must be logged in to submit this form.
Findings
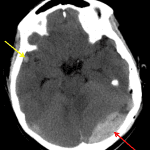
- Acute nondisplaced left parietal bone fracture extending into the left lambdoid suture with mild sutural diastasis
- Subjacent epidural hematoma measuring up to 2 cm in thickness
- Associated mass effect with crowding of the ambient and quadrigeminal cisterns, crowding of the fourth ventricle, and mild upward and downward bulging of the posterior fossa structures without frank herniation
- Small hemorrhagic contusion in the right anterior temporal lobe
- Left parietal scalp hematoma, a portion of which is likely subgaleal, with intermixed locules of gas
- Mucosal thickening of the paranasal sinuses with near complete opacification of the left sphenoid sinus
Diagnosis
- Epidural hematoma
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Acute nondisplaced left parietal bone fracture extending into the left lambdoid suture with mild sutural diastasis. Subjacent epidural hematoma measuring up to 2 cm in thickness. Small hemorrhagic contusion in the right anterior temporal lobe compatible with contrecoup injury.
Corresponding mass effect in the posterior fossa without frank herniation or hydrocephalus at this time. However, recommend attention on short interval followup imaging.
Mucosal thickening of the paranasal sinuses with near complete opacification of the left sphenoid sinus, which can be seen with acute sinusitis.
Discussion
- Epidural hematomas represent bleeding between the dura and the inner table of the calvarium
- These are typically arterial, with the middle meningeal artery being the most common offender, but venous epidural hemorrhage is also possible. Here are some common locations for venous epidural hemorrhage:
- Vertex: fracture and/or sagittal suture diastasis -> superior sagittal sinus injury -> epidural hematoma crossing the suture and inferiorly displacing the sinus
- Anterior middle cranial fossa: due to hemorrhage from the sphenoparietal sinus, can be managed conservatively
- Posterior fossa adjacent to an occipital fracture: often related to sinus (especially transverse sinus) injury
- Most are associated with skull fractures
- Epidural hematomas can rapidly expand leading to herniation and death. “Swirling” low density within the hematoma (which is arguably present to some degree in this case) indicates non-clotted fresh blood mixing in with the clotted blood and is concerning for ongoing bleeding
- Epidural hematomas are less common in elderly patients due to increased adherence of the dura to the skull with age
- Epidural hematomas respect suture lines where the periosteal component of the dura extends through the skull. There is one major exception to this: if the suture is disrupted (e.g. if it is diastatic on imaging or if a fracture extends through a suture), then the hematoma can cross suture lines. Notice that the hematoma extends across the diastatic lambdoid suture in this case
- Always look for contrecoup injuries. These are most commonly seen involving the temporal poles and inferior frontal lobes
📣 Feedback?
⌨️ Keyboard Shortcuts ("K")
Help | Terms | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
Medical Disclaimer | © 2024 CaseStacks LLC
Related Cases
Temporarily disabled.
References
- Fink KR. Imaging of head trauma. Seminars in Roentgenology 2016; 51(3): 143-151.
- Gean AD, Fischbein NJ, Purcell DD, Aiken AH, Manley GT, Stiver SI. Benign anterior temporal epidural hematoma: indolent lesion with a characteristic CT imaging appearance after blunt head trauma. Radiology 2010; 257: 212-218.


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
