Age: 24
Sex: Female
Indication: Trauma
Save ("V")
Case #1
Findings
Chest Radiograph
- Acute nondisplaced right first rib fracture.
- No pleural effusion or pneumothorax.
- Mild hazy bibasilar opacities.
CT
- Chest
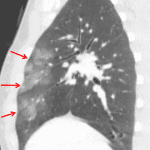
- Mild peripheral groundglass opacities in the anterior aspects of the right upper and middle lobes and to a lesser extent in the lingula
- Trace bilateral pneumothoraces
- Trace anterior pneumomediastinum
- Residual thymus in the anterior mediastinum
- Abdomen/Pelvis
- No acute findings
- Narrowing and inferior deviation at the origin of the celiac artery with poststenotic dilation
- MSK
- Acute nondisplaced fractures of the right first rib and of the left fifth through eighth ribs
- Acute L1 compression fracture with approximately 10% anterior height loss and no bony retropulsion
- Possible additional acute compression fracture of the T11 vertebral body without significant height loss or bony retropulsion
- Mild offset of the coccygeal segments
Diagnosis
- Pulmonary contusion
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Acute nondisplaced fractures of the right first and left fifth through eighth ribs. Trace bilateral pneumothoraces.
Trace anterior pneumomediastinum without mediastinal hematoma or evidence of aortic trauma.
Pulmonary contusion in the anterior aspects of the right upper and middle lobes and to a lesser extent in the lingula.
Acute L1 and possibly T11 compression fractures with minimal height loss and no bony retropulsion.
Age-indeterminate mild offset of the coccygeal segments which may be traumatic or developmental.
No acute traumatic findings in the abdominopelvic cavity.
Narrowing at the origin of the celiac artery likely relates to median arcuate ligament compression. Though often asymptomatic, this finding can be a cause for chronic abdominal pain.
Discussion
- Pulmonary contusion is often located in a non-dependent area of the lung and correlates with the site(s) of blunt chest trauma
- Pulmonary contusion will typically resolve within a few days with supportive management, so if you see groundglass opacities persisting a week or more after trauma or appearing more than 24 hours after trauma, there is likely something else going on
- If you see bilateral dependent groundglass opacities, this is more likely to represent subsegmental atelectasis or aspiration
- Make sure to look for associated pulmonary laceration or pneumatocele
- In this case, the trace pneumomediastinum is likely a product of the Macklin effect: gas released from alveolar rupture tracks along bronchovascular bundles back to the mediastinum
- However, whenever you see pneumomediastinum, make sure to look closely for evidence of tracheobronchial or esophageal injury and look for other signs of mediastinal trauma including mediastinal hematomas and aortic injuries


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
