Age: 59
Sex: Male
Indication: Trauma
Save ("V")
Case #1
Findings
- Chest
- Small lower anterior mediastinal hematoma without active extravasation
- Trace right pneumothorax
- Mild contusion in the anterior aspect of the left upper lobe
- Mild dependent bilataral lower lobe atelectasis
- Small hiatal hernia
- Abdomen/Pelvis
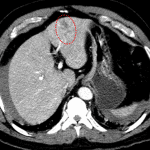
- Hepatic laceration involving segments 2/3 measuring 4.4 cm in greatest span. No extension to the hilum or evidence of active hemorrhage
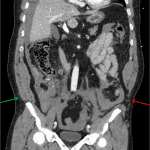
- Moderate volume hemoperitoneum, particularly concentrated about the liver and in the right paracolic gutter
- Stranding in the right ileocolic and left colic mesentery with areas of associated contrast density which change in size and appearance on delayed images
- MSK
- Acute nondisplaced fractures of the right lateral third and fourth ribs
- Acute minimally displaced fractures through the costal cartilage of multiple right ribs
- Remote right lateral eighth and ninth rib fractures
- Acute minimally displaced fracture of the xiphoid process
- Acute minimally displaced fracture of the anterior superior corner of the L4 vertebral body.
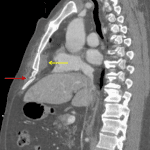
- Traumatic rupture of all fascial layers of the left lateral abdominal wall near their attachment on the left iliac crest resulting in a lumbar hernia, which only contains fat
- Intramuscular hematoma in the imaged portion of the left sternocleiodomastoid muscle
- Soft tissue contusion anterior to the sternum
Diagnosis
- Hepatic laceration
- Mesenteric injuries with active hemorrhage
- Mediastinal hematoma
- Traumatic lumbar hernia
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Traumatic hematomas in the right ileocolic and left colic mesenteries with evidence of active hemorrhage at both locations.
Grade 3 hepatic laceration in segments 2/3 with moderate volume hemoperitoneum.
Acute left lumbar hernia with herniation of abdominal fat through the defect.
Acute fractures through the right costal cartilage and xiphoid process with a small lower mediastinal hematoma. No direct evidence of acute aortic injury.
Acute nondisplaced fractures of the right lateral third and fourth ribs with a tiny right pneumothorax.
Acute minimally displaced fracture of the anterior superior corner of the L4 vertebral body.
Partially imaged intramuscular hematoma in the left sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Discussion
- Hepatic injuries can be classified using the AAST system, as shown in the table below. While including the classification of injuries is not always important, it is important to generate reports that will be meaningful to your referring surgeons.
- Any time you see a laceration or hematoma, make sure to compare closely between arterial and delayed phases for signs of arterial injury including hemorrhage (should get larger and less poorly defined on delayed phase) and pseudoaneurysm (should remain similar in appearance on delayed phase)
- When you see a laceration that extends to or near the hepatic hilum, make sure to look for biliary complications which can include:
- Hemorrhage into a bile duct causing obstruction – look for regional intrahepatic duct dilation
- Bile leak, which will initially look like nonloculated low density fluid, but will progress to a biloma over time
- This case also shows a good example of a traumatic lumbar hernia, as shown in an annotated image below. While rare, these indicate severe shearing forces and can unfortunately easily be missed by clinicians and radiologists in polytrauma cases
AAST Liver Injury Scale
| Grade | Laceration | Subcapsular hematoma | Parenchymal hematoma | Major vascular injury |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | < 1 cm in depth | < 10% of the hepatic surface area | None | None |
| II | 1-3 cm in depth | 10-50% of the hepatic surface area | < 10 cm in diameter | None |
| III | > 3 cm in depth | > 50% of the hepatic surface area Expanding Ruptured |
> 10 cm in diameter Expanding Ruptured |
Active bleeding confined within the liver |
| IV | Disruption of 25-75% of a lobe (or 1-3 segments of a lobe) | Any | Any | Active bleeding extending beyond the liver |
| V | Disruption of > 75% of a lobe (or > 3 segments of a lobe) | Any | Any | Juxtahepatic venous injury (IVC or central hepatic veins) |
| VI | Any | Any | Any | Avulsion of the hepatic hilum |


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
