- Key Images
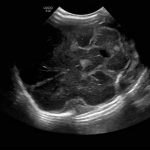
- L Sagittal
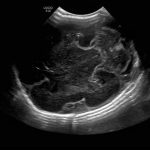
- R Sagittal
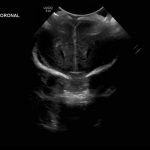
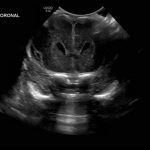
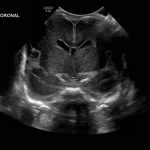
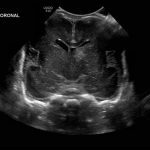
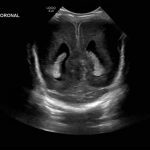
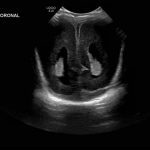
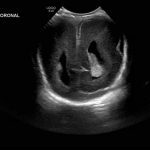
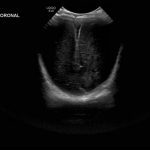
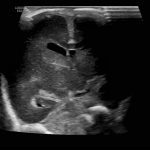
- Coronal
Press "A" to view the previous image and "D" for the next image.
Screenshot (48)
Screenshot (49)
Screenshot (50)
Screenshot (51)
Screenshot (52)
Screenshot (53)
Screenshot (54)
Screenshot (55)
Screenshot (56)
Screenshot (57)
Screenshot (58)
Screenshot (59)
Screenshot (60)
Screenshot (61)
Screenshot (62)
Screenshot (63)
Screenshot (64)
Screenshot (65)
Screenshot (66)
Screenshot (67)
Screenshot (68)
Screenshot (69)
Screenshot (70)
Screenshot (71)
Screenshot (72)
Screenshot (73)
Screenshot (74)
Screenshot (75)
Screenshot (76)
Screenshot (77)
Screenshot (78)
The requested content cannot be found
Age: 4 days (born at 24 weeks)
Sex: Male
Indication: Evaluate for germinal matrix hemorrhage
Save ("V")
Case #1
You must be logged in to submit this form.
Findings
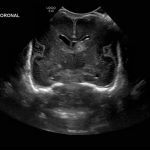
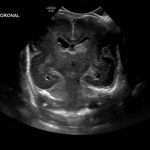
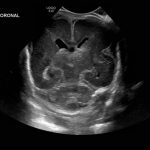
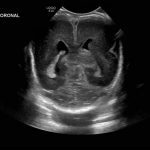
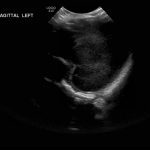
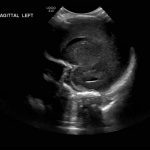
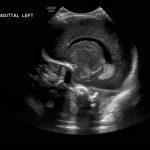
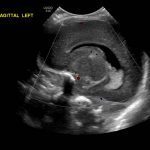
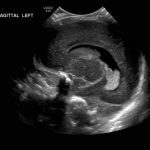
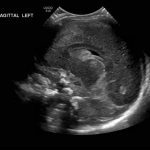
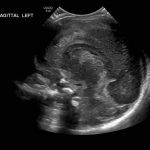
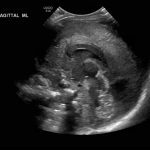
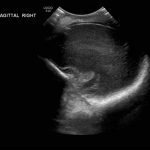
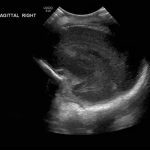
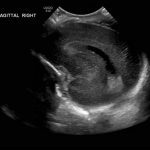
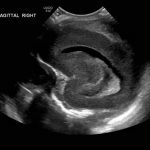
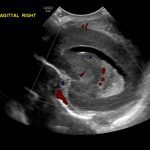
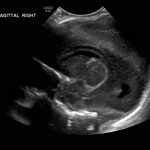
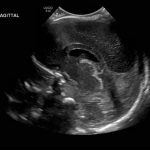
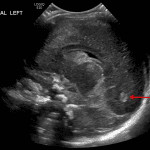
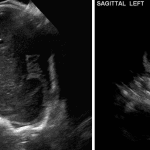
- Echogenic material in the left caudothalamic groove and layering in the occipital horn of the left lateral ventricle
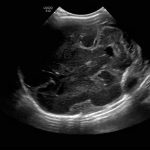
- No ventriculomegaly
- No abnormal brain parenchymal echogenicity or extra-axial collections
- Premature sulcation pattern
Diagnosis
Grade 2 germinal matrix hemorrhage
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Left germinal matrix hemorrhage involving the caudothalamic groove and layering in the occipital horn of the left lateral ventricle without hydrocephalus (grade 2).
No abnormal brain parenchymal echogenicity or extra-axial collections.
Premature sulcation pattern.
Discussion
- The germinal matrix is a highly vascularized subependymal structure that is at risk for bleeding as a result of perinatal stress
- The germinal matrix regresses in the third trimester. It is confined to the caudothalamic groove by 32 weeks and essentially gone by 36 weeks – therefore, the risk for germinal matrix hemorrhage is essentially zero in infants born after 36 weeks and conversely greatly increased in infants born at less than 32 weeks postmenstrual age
- Because symptoms may not be revealing, screening neurosonography is recommended in infants born at less than 30 weeks postmenstrual age
- When looking for germinal matrix hemorrhage, remember that the choroid plexus (which is unfortunately echogenic, similar to hemorrhage) should not extend anterior to the caudothalamic groove, so echogenic material in the frontal horns is likely hemorrhage
- Here are the 4 grades of germinal matrix hemorrhage:
Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage
| Grade | Hemorrhage location | Hydrocephalus |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confined to caudothalamic groove | Absent |
| 2 | Intraventricular hemorrhage | Absent |
| 3 | Intraventricular hemorrhage | Present |
| 4 | Intraparenchymal hemorrhage | Absent/Present |
- Hydrocephalus – here are some approximate normal measurement standards on ultrasound (from Brouwer et al.). Examples of these measurements are demonstrated in the annotated images below
- Ventricular index (distance from the lateral wall of the frontal horn to the falx measured in the coronal plane) < 10 mm at 25-30 weeks and < 15 mm at 40 weeks
- Anterior horn width (greatest diagonal width of the frontal horn measured in the coronal plane) < 3 mm at 25-30 weeks and < 4 mm at 40 weeks
- Thalamo-occipital distance (distance from the posterior margin of the thalamus to the posterior margin of the occipital horn measured in the parasagittal plane) < 20 mm at 25-30 weeks and < 25 mm at 40 weeks
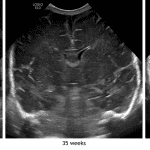
- As the brain matures, sulci become deeper and more numerous
- Recognizing normal sulcation patterns for patient age can be useful in early diagnosis of disorders of cortical development like lissencephaly
- Large sulci/fissures become apparent early in development (e.g. the sylvian fissures and parietooccipital sulci) while smaller sulci may not become apparent by ultrasound until late in the third trimester
- Refer to the annotated image below to see the differences in sulcation between this patient and patients imaged at 35 and 42 weeks postmenstrual age
📣 Feedback?
⌨️ Keyboard Shortcuts ("K")
Help | Terms | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
Medical Disclaimer | © 2024 CaseStacks LLC
Related Cases
Temporarily disabled.
References
- Bhat V, Bhat V. Neonatal neurosonography: A pictorial essay. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2014; 24(4): 389-400.
- Brouwer MJ, de Vries LS, Groenendaal F, Koopman C, Pistorius LR, Mulder EJ, Benders MJNL. New reference values for the neonatal cerebral ventricles. Radiology 2012; 262: 224-233.
- Chen X, Li SL, Luo GY, Norwitz ER, Ouyang SY, Wen HX, Yuan Y, Tian XX, He JM. Ultrasonographic characteristics of cortical sulcus development in the human fetus between 18 and 41 weeks of gestation. Chin Med J (Engl) 2017; 130(8): 920-928.


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
